In this week’s eSkeptic, David Cowan reviews Logicomix: An Epic Search for Truth, a graphic novel about the life and ideas of philosopher and mathematician Bertrand Russell, written by Apostolos Doxiadis and Christos H. Papadimitriou.
David Cowan and his family live near Kepler’s bookstore in Menlo Park, California. David blogs about science and superstition at WhoHasTimeForThis.com, sings a capella with Voices in Harmony, and invests in technology startups for Bessemer Venture Partners. Recently, on a flight from St. Petersburg, David taught himself to draw cartoons using Microsoft Powerpoint.
LogiComix: An Epic Search for Truth
(with a Connection in Frankfurt)
by David Cowan
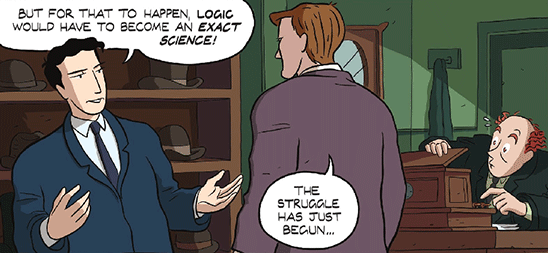
Normally I’d wait until I finish reading a book before I write my review. But LogiComix is — er, unusual, and not just because it’s a graphic novel about a dead logician. Three chapters into it, I’m captivated and enchanted by the playful, clever, innovative use of self-reference. For example, the prologue opens with co-author Apostolos Doxiadis reading a draft of his story. As we intrude upon his thoughts, he invites us to meet Berkeley computer scientist Christos Papadimitriou, whom Apostolos must recruit to help him with the book. When Apostolos tells Christos the story he’d like to craft, we, the readers, get to hear it too! Along the way, Christos asks questions, points out problems, and makes suggestions to Apostolos as well as to his illustrators Alecos Papadatos and Annie di Donna. As the story unfolds, the creative team debate how to best move it forward. By the end Christos and we together come to understand that LogiComix is deliberately not LOGIC FOR DUMMIES, but rather a true story about passion, family, war, love, tragedy and hope.

So if the LogiComix creative team can be characters writing their story as it goes, then I can do the same in this review. If that violates some rule, I wouldn’t know because I am in no way a professional book reviewer. Here are my only qualifications for writing this review:
- I have a fancy degree in theoretical computer science centered mainly on the works of those logicians portrayed in this story.
- I am a practiced blogger, so I can emulate authority on any subject.
- My dear friend Vivian Leal of Kepler’s Bookstore asked me to review this book.
- As I type, I am on a Lufthansa flight from St. Petersburg heading home to San Francisco, so I have some time.
When Vivian asked me to review LogiComix, I readily agreed. Not only do I love both Vivian and Kepler’s, but I can also say that I love Christos Papadimitriou. I’ve never met him, but he did also happen to co-author my favorite college textbook Elements of the Theory of Computation, a beautifully elegant introduction to Turing machines and recursion that even I could understand. His co-author back then was Harry Lewis, my CS121 professor and also my undergraduate advisor. (Still, like Papadimitriou, Lewis never knew who I was, though once he passed me by in Harvard Yard and raised his eyebrows at me in an acknowledging way that made me feel a real connection.) Coincidentally, I would have never met Vivian had I not befriended her husband Daniel 23 years ago back in CS121 — another debt I owe Christos Papadimitriou.

So far, the graphic novel format of LogiComix (now popularized by the Wimpy Kid and Maus series, as well as The Invention of Hugo Cabret) is working well for me. The throwback to comic books promises to make even Boolean Algebra an accessible topic to all, just as Scott McCloud recently did with a comic book about Google’s new Chrome browser architecture. But more importantly, Apostolos draws us into the story with visuals that not only support the narrative but also relay sub-plots and emotional texture. Often we see a human side to the characters that they otherwise don’t acknowledge, such as a jealous look from a wife, or a 12-year-old boy subtly covering his lap while his beautiful French nanny reads him a love sonnet. (I’m reminded of the beautiful French nanny who charmed me as well — so much so that I married her. Hmm, can’t this plane fly any faster?)
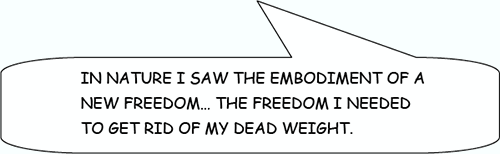
The excited 12-year-old is our hero — the great mathematician Bertrand Russell who devoted not only his career but his life to the pursuit of a provably logical foundation for mathematics, as Euclid had purportedly done for geometry (at least before Lobachewski and Riemann each had his way with Euclid’s assumptions). Embedding yet another layer of recursion into LogiComix, Russell tells his own story in the form of a lecture delivered at an American university on Sept 4, 1939, the day the UK joined World War II. The lecture, titled “The Role of Logic in Human Affairs” promises an answer to the question hurled at him by isolationists as to whether Russell, as a World War I conscientious objector, supports the war this time around.
Russell’s own account of his childhood is a contrasting story of privilege and borderline abuse. Orphaned as an infant, “Bertie” lived with his grandfather — a former British prime minister — and a domineering grandmother who imprisoned Bertie in rules and superstitions. Eventually Bertie discovered the family secret that madness had taken his father’s life and disabled his uncle. So when he learned geometry — constructed proof by proof upon common sense and reason — BERTRAND embraced logic and science as tools to not only understand the world, but to preserve his own sanity.
Bertrand Russell’s Epic Search for Truth
Russell studies mathematics at Cambridge University, and proceeds to seek out the great minds of his time, to find some articulation and validation of the basic tenets underlying mathematics. Russell overcomes his shyness to engage the greatest professors of his time with his questions (a thrill I remember well from studying the Sacks Theorem of recursion theory from Professor Sacks himself).
Russell’s travels take him to Germany just 10 minutes before my Lufthansa pilot announces our imminent arrival in Frankfurt, where I’ll make my connection to San Francisco. Russell’s account of those days in Germany evokes that nation’s unique capacity for both logic and madness. There he meets his future best friend, housemate and collaborator Alfred Whitehead, who had created the first formal system for algebra. He meets Gottlob Frege, who had founded modern logic studies by introducing the concept of Boolean variables, though eventually Frege becomes paranoid, and as early as 1925 starts ranting about a Final Solution for the” Jewish problem.” Finally RUSSELL meets Georg Cantor, inventor of Set Theory, who was already then losing his mind.

The interplay of logic and madness is a recurring theme of LogiComix, as Russell struggles to stave off madness himself (with only partial success, as readers will learn).
Another recurring theme of the story is Russell’s failures at love, as he depends solely on logic to master courtship, marriage and child-rearing, even as everyone around him succumbs to irrationality. His memoirs — humble and candid –recount his nerdy fumbles followed by his inconsiderate prioritization of work over family. (That reminds me — I’ll use my layover in Frankfurt to call my family. Today is the kids’ first day of school, and they should know how proud I am.)
As Russell strives to formalize the logic behind math, he gravitates toward set theory, until he himself has an epiphany now known as Russell’s Paradox, which can be simplified to this question: Does the catalog of all books (and book reviews!) that do NOT exhibit self-reference include itself in the listing? Either answer leads to a logic contradiction. Russell’s Paradox deflates everyone who has been working on Set Theory. RUSSELL was surprised that Cantor himself takes the paradox as a sign from God.

As Russell embarks on his epic search for truth, he continues to engage the greatest minds of the century, but along the way he must navigate wars, women (enticing but difficult) and the madness that often accompanies logical genius. At one point he mentors the young Ludwig Wittgenstein, the renowned philosopher and father of cognitive psychology. Ultimately, poor mental health ravages Wittgenstein’s family, and Wittgenstein dismisses Russell’s call for formalizing mathematics as irrelevant to the real world.

Having made my connection out of Frankfurt, I’m now traversing the Continent just as Russell recounts his own travel through France, where he engages Klein, Dedekind, Poincare and Hilbert. I must confess that I didn’t learn (or remember) Hilbert’s work, and LogiComix fails to impart an intuitive understanding of his philosophy. Now that I think of it, the story fails to explain the work of any of the great logicians, so unless you already know the ideas, you’re somewhat in the dark as to how they relate to Russell’s search. (For example, the characters don’t explain how an infinite set can be countable.) Having said that, I can’t protest too much because Papadimitrious himself complains about this in the story. Apostos insists that the story should trump the math.
[What I learned only upon finishing the book is that it does come with a terrific glossary that expounds upon the thinkers and their work. I wish I had known about it while I was reading the story. You’re now duly notified.]
Russell spends many years working and living with Whitehead trying to adapt Set Theory to overcome his paradox, but Volume II of their Principia Mathematica is interrupted by Russell’s greatest professional setback — Kurt Godel’s delivery of the Incompleteness Theorem. Essentially Godel proves the futility of a developing a formal system of logic rich enough to represent arithmetic by showing how one can formulate a paradox for any such system. Although Apostos and Papadimitriou mention this in the glossary, I wish the story itself explained how Godel himself used recursion to prove his theorem. It is really the most beautiful proof I have ever seen, and to this day I remember that moment in Math 141 when we reached the end of this proof. For weeks we had been learning Godel’s scheme for symbolically representing arithmetic concepts and applying obscure theorems (e.g. the “Pigeonhole Principle”) that took us in bizarre directions. But on that last day, the bits and pieces all magically converged into an inescapable conclusion. I got those goosebumps you get when you witness someone stretch the limits of human ability.
But in a way Godel’s Theorem liberates Russell, who redirects his logical faculties to more worldly affairs. Apostos brings it all home when Russell shares his life’s lessons with the American audience. (Judging from the view, I believe that I’m now back in the States as well!)
Influential and Similar Works
LogiComix marries the elements of many great works. Obviously, Apostos explores and uses self-reference in much the same way as Houfstadter’s masterpiece Godel Escher Bach: An Eternal Golden Braid. Another clear influence is Kurt Vonnegut, whose book SlaughterHouse Five featured the author’s voice in a similar lament of the madness behind World War II. At one point, Papadimitriou even mentions Vonnegut’s Breakfast of Champions to exemplify a self-referential novel.
Milton Steinberg’s As A Driven Leaf, about the Talmudic rabbi Elisha ben Abuyah who actually lived around the turn of the second century, tells a similar tale of an epic search for truth. Elisha rejects Judaism in favor of Greek logic, only to regret it in the end. But while Russell must ultimately concede the limitations of logic, he would never return to his grandmother’s superstitions. In fact when Whitehead’s son was killed in the war, RUSSELL couldn’t even attend the funeral.

Although surely not an influence here, Caveh Zahedi’s hilarious, racy film I Am A Sex Addict would, I believe, also appeal to many LogiComix fans. Like LogiComix, it liberally uses real time self-reference to document the hero’s lusty mishaps with women, and the lessons he learns about love.
So LogiComix is part Godel-Escher-Bach, part As a Driven Leaf, part I Am a Sex Addict, and of course part Tintin.
The Fundamental Question: What Makes A Good Book?
Must it be engaging, provocative, emotional, beautiful, instructional, or right? Or some combination of the above? There is no universal answer. But acknowledging this incompleteness allows us to take the next step — to use the tools we have to assess each book independently (which gives you a hint as to what Russell’s told his audience of pacifists in 1941). So if I learned anything from LogiComix, I learned that I needn’t answer the fundamental question in order to recommend it. This is a story that engages, provokes and instructs the reader. But more importantly, I liked it.
So now that the flight attendant is insisting that I stow
The latest additions to MichaelShermer.com and SkepticBlog.org

NEW ON MICHAELSHERMER.COM
Paranoia Strikes Deep
From JFK to 9/11, conspiracy theories abound. In his September 2009 column for Scientific American, Michael Shermer delves into the foundations of conspiratorial cognition in answer to the question of why people believe highly improbable conspiracies. • READ the column •
NEW ON SKEPTICBLOG.ORG
What I Believe
Michael Shermer shares with readers why he believes in science and the power of humanity. • READ the blog post •